අක්ෂර ක්රම
A writing system is a type of symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.
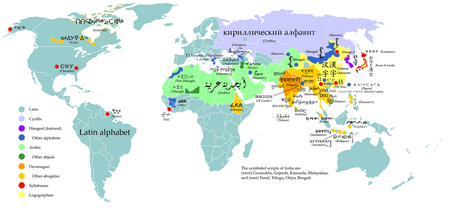
General properties
සංස්කරණයWriting systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that one must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to comprehend the text. By contrast, other possible symbolic systems such as information signs, painting, maps, and mathematics often do not require prior knowledge of a spoken language.
Every human community possesses language, a feature regarded by many as an innate and defining condition of mankind. However the development of writing systems, and the process by which they have supplanted traditional oral systems of communication has been sporadic, uneven and slow. Once established, writing systems on the whole change more slowly than their spoken counterparts, and often preserve features and expressions which are no longer current in the spoken language. The great benefit of writing systems is their ability to maintain a persistent record of information expressed in a language, which can be retrieved independently of the initial act of formulation.
All writing systems require:
- a set of defined base elements or symbols, individually termed characters or graphemes, and collectively called a script;
- a set of rules and conventions understood and shared by a community, which arbitrarily assign meaning to the base elements, their ordering, and relations to one another;
- a language (generally a spoken language) whose constructions are represented and able to be recalled by the interpretation of these elements and rules;
- some physical means of distinctly representing the symbols by application to a permanent or semi-permanent medium, so they may be interpreted (usually visually, but tactile systems have also been devised).
Basic terminology
සංස්කරණයThe study of writing systems has developed along partially independent lines in the examination of individual scripts, and as such the terminology employed differs somewhat from field to field.
The generic term text may be used to refer to an individual product of a writing system. The act of composing a text may be referred to as writing, and the act of interpreting the text as reading. In the study of writing systems, orthography refers to the method and rules of observed writing structure (literal meaning, "correct writing"), and in particular for alphabetic systems, includes the concept of spelling.
A grapheme is the technical term coined to refer to the specific base or atomic units of a given writing system. Graphemes are the minimally significant elements which taken together comprise the set of "building blocks" out of which texts of a given writing system may be constructed, along with rules of correspondence and use. The concept is similar to that of the phoneme used in the study of spoken languages. For example, in the Latin-based writing system of standard contemporary English, examples of graphemes include the majuscule and minuscule forms of the twenty-six letters of the alphabet (corresponding to various phonemes), marks of punctuation (mostly non-phonemic), and a few other symbols such as those for numerals (logograms for numbers).
Note that an individual grapheme may be represented in a wide variety of ways, where each variation is visually distinct in some regard, but all are interpreted as representing the "same" grapheme. These individual variations are known as allographs of a grapheme (compare with the term allophone used in linguistic study). For example, the minuscule letter a has different allographs when written as a cursive, block, or typed letter. The selection between different allographs may be influenced by the medium used, the writing instrument, the stylistic choice of the writer, and the largely unconscious features of an individual's handwriting.
The terms glyph, sign and character are sometimes used to refer to a grapheme. Common usage varies from discipline to discipline; compare cuneiform sign, Maya glyph, Chinese character. The glyphs of most writing systems are made up of lines (or strokes) and are therefore called linear, but there are glyphs in non-linear writing systems made up of other types of marks, such as Cuneiform and Braille.
Writing systems are conceptual systems, as are the languages to which they refer. Writing systems may be regarded as complete according to the extent to which they are able to represent all that may be expressed in the spoken language.
History of writing systems
සංස්කරණයWriting systems were preceded by proto-writing, systems of ideographic and/or early mnemonic symbols. The best known examples are:
- Jiahu Script, symbols on tortoise shells in Jiahu, ca. 6600 BC
- Vinča script (Tărtăria tablets), ca. 4500 BC
- Early Indus script, ca. 3500 BC
The invention of the first writing systems is roughly contemporary with the beginning of the Bronze Age in the late Neolithic of the late 4th millennium BC. The Sumerian archaic cuneiform script and the Egyptian hieroglyphs are generally considered the earliest writing systems, both emerging out of their ancestral proto-literate symbol systems from 3400–3200 BC with earliest coherent texts from about 2600 BC.
Though the Ge'ez writing system of Ethiopia is considered Semitic it is likely of semi-independent origin, having roots in the Meroitic Sudanese ideogram system.[1]
The Chinese script likely developed independently of the Middle Eastern scripts, around 1600 BC.
The pre-Columbian Mesoamerican writing systems (including among others Olmec and Maya scripts) are also generally believed to have had independent origins.
It is thought that the first true alphabetic writing appeared around 2000 BC, as a representation of language developed for Semitic slaves in Egypt by Egyptians (see History of the alphabet). Most other alphabets in the world today either descended from this one innovation, many via the Phoenician alphabet, or were directly inspired by its design.
Functional classification of writing systems
සංස්කරණයThe oldest-known forms of writing were primarily logographic in nature, based on pictographic and ideographic elements. Most writing systems can be broadly divided into three categories: logographic, syllabic, and alphabetic (or segmental); however, all three may be found in any given writing system in varying proportions, often making it difficult to categorise a system uniquely. The term complex system is sometimes used to describe those where the admixture makes classification problematic.
| Type | Each symbol represents | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Logographic | morpheme | Chinese characters |
| Syllabic | syllable | Japanese kana |
| Alphabetic | phoneme (consonant or vowel) | Latin alphabet |
| Abugida | phoneme (consonant+vowel) | Indian Devanāgarī |
| Abjad | phoneme (consonant) | Arabic alphabet |
| Featural | phonetic feature | Korean hangul |
Logographic writing systems
සංස්කරණයA logogram is a single written character which represents a complete grammatical word. Most Chinese characters are classified as logograms.
As each character represents a single word (or, more precisely, a morpheme), many logograms are required to write all the words of language. The vast array of logograms and the memorization of what they mean are the major disadvantage of the logographic systems over alphabetic systems. However, since the meaning is inherent to the symbol, the same logographic system can theoretically be used to represent different languages. In practice, this is only true for closely related languages, like the Chinese languages, as syntactical constraints reduce the portability of a given logographic system. Japanese uses Chinese logograms extensively in its writing systems, with most of the symbols carrying the same or similar meanings. However, the semantics, and especially the grammar, are different enough that a long Chinese text is not readily understandable to a Japanese reader without any knowledge of basic Chinese grammar, though short and concise phrases such as those on signs and newspaper headlines are much easier to comprehend.
While most languages do not use wholly logographic writing systems many languages use some logograms. A good example of modern western logograms are the Hindu-Arabic numerals — everyone who uses those symbols understands what 1 means whether he or she calls it one, eins, uno, yi, ichi or ehad. Other western logograms include the ampersand &, used for and, the at sign @, used in many contexts for at, the percent sign % and the many signs representing units of currency ($, ¢, €, £, ¥ and so on.)
Logograms are sometimes called ideograms, a word that refers to symbols which graphically represent abstract ideas, but linguists avoid this use, as Chinese characters are often semantic–phonetic compounds, symbols which include an element that represents the meaning and element that represents the pronunciation. Some nonlinguists distinguish between lexigraphy and ideography, where symbols in lexigraphies represent words, and symbols in ideographies represent words or morphemes.
The most important (and, to a degree, the only surviving) modern logographic writing system is the Chinese one, whose characters are or were used, with varying degrees of modification, in Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, and other east Asian languages. Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs and the Mayan writing system are also systems with certain logographic features, although they have marked phonetic features as well, and are no longer in current use.
Syllabic writing systems
සංස්කරණයAs logographic writing systems use a single symbol for an entire word, a syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent (or approximate) syllables, which make up words. A symbol in a syllabary typically represents a consonant sound followed by a vowel sound, or just a vowel alone.
In a "true syllabary", there is no systematic graphic similarity between phonetically related characters (though some do have graphic similarity for the vowels). That is, the characters for "ke", "ka", and "ko" have no similarity to indicate their common "k"-ness. However, another type of syllabic writing system is known as the abugida, where each grapheme typically represents a syllable, but where the characters representing related sounds are similar graphically (typically, a common consonantal base is annotated in a more or less consistent manner to represent the vowel in the syllable). The nomenclature used to make this distinction was only introduced by linguists relatively recently, borrowing the term abugida from Ethiopian languages that call their own Ge'ez script by this name.
Syllabaries are best suited to languages with relatively simple syllable structure, such as Japanese. The English language, on the other hand, allows complex syllable structures, with a relatively large inventory of vowels and complex consonant clusters, making it cumbersome to write English words with a syllabary. To write English using a syllabary, every possible syllable in English would have to have a separate symbol, and whereas the number of possible syllables in Japanese is no more than about fifty to sixty, in English there are many thousands.
Other languages that use true syllabaries include Mycenaean Greek (Linear B) and Native American languages such as Cherokee. Several languages of the Ancient Near East used forms of cuneiform, which is a syllabary with some non-syllabic elements.
Alphabetic writing systems
සංස්කරණයAn alphabet is a small set of letters — basic written symbols — each of which roughly represents or represented historically a phoneme of a spoken language. The word alphabet is derived from alpha and beta, the first two symbols of the Greek alphabet.
In a perfectly phonemic alphabet, the phonemes and letters would correspond perfectly in two directions: a writer could predict the spelling of a word given its pronunciation, and a speaker could predict the pronunciation of a word given its spelling. Each language has general rules that govern the association between letters and phonemes, but, depending on the language, these rules may or may not be consistently followed.
Perfectly phonemic alphabets are very easy to use and learn, and languages that have them (for example Serbocroatian or Finnish) have much lower barriers to literacy than languages such as English, which has a very complex and irregular spelling system. As languages often evolve independently of their writing systems, and writing systems have been borrowed for languages for which they were not designed, the degree to which letters of an alphabet correspond to phonemes of a language varies greatly from one language to another and even within a single language. In modern times, when linguists invent a writing system for a language that didn't previously have one, the goal is usually to develop a phonemic alphabet. It should be noted that a truly phonetic alphabet for a natural spoken language would be very cumbersome, as it would have to have a huge variety of phonetic variation. An example of such a writing system is the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA).
Abjads
සංස්කරණයThe first type of alphabet that was developed was the abjad. An abjad is an alphabetic writing system where there is one symbol per consonant. Abjads differ from other alphabets in that they have characters only for consonantal sounds. Vowels are not usually marked in abjad.
All known abjads (except maybe Tifinagh) belong to the Semitic family of scripts, and derive from the original Northern Linear Abjad. The reason for this is that Semitic languages and the related Berber languages have a morphemic structure which makes the denotation of vowels redundant in most cases.
Some abjads (such as Arabic and Hebrew) have markings for vowels as well, but use them only in special contexts, such as for teaching. Many scripts derived from abjads have been extended with vowel symbols to become full alphabets, the most famous case being the derivation of the Greek alphabet from the Phoenician abjad. This has mostly happened when the script was adapted to a non-Semitic language.
The term abjad takes its name from the old order of the Arabic alphabet's consonants Alif, Bá, Jim, Dál, though the word may have earlier roots in Phoenician or Ugaritic.
Abjad is still the word for alphabet in Arabic, Malay, and Indonesian.
Abugidas
සංස්කරණයAn abugida is an alphabetic writing system whose basic signs denote consonants with an inherent vowel and where consistent modifications of the basic sign indicate other following vowels than the inherent one.
Thus, in an abugida there may or may not be a sign for "k" with no vowel, but also one for "ka" (if "a" is the inherent vowel), and "ke" is written by modifying the "ka" sign in a way that is consistent with how one would modify "la" to get "le". In many abugidas the modification is the addition of a vowel sign, but other possibilities are imaginable (and used), such as rotation of the basic sign, addition of diacritical marks, and so on.
The contrast with "true syllabaries" is that the latter have one distinct symbol per possible syllable, and the signs for each syllable have no systematic graphic similarity. The graphic similarity of most abugidas comes from the fact that they are derived from abjads, and the consonants make up the symbols with the inherent vowel, and the new vowel symbols are markings added on to the base symbol.
In the Ge'ez script, for which the linguistic term abugida was named, the vowel modifications do not always appear systematic, although they originally were more so. Canadian Aboriginal syllabics can be considered abugidas, although they are rarely thought of in those terms. The largest single group of abugidas is the Brahmic family of scripts, however, which includes nearly all the scripts used in India and අග්නිදිග ආසියාව.
The name abugida is derived from the first four characters of an order of the Ge'ez script used in some contexts. It was borrowed from Ethiopian languages as a linguistic term by Peter T. Daniels.
Featural writing systems
සංස්කරණයA featural script represents finer detail than an alphabet. Here symbols do not represent whole phonemes, but rather the elements (features) that make up the phonemes, such as voicing or its place of articulation. Theoretically, each feature could be written with a separate letter; and abjads or abugidas, or indeed syllabaries, could be featural, but the only prominent system of this sort is Korean hangul. In hangul, the featural symbols are combined into alphabetic letters, and these letters are in turn joined into syllabic blocks, so that the system combines three levels of phonological representation.
Ambiguous systems
සංස්කරණයMost writing systems are not purely one type. The English writing system, for example, includes numerals and other logograms such as #, $, and &, and the phonetic letters are a poor match to sound. As mentioned above, all logographic systems have phonetic components as well, whether that's along the lines of a syllabary, such as Chinese ("logo-syllabic"), or an abjad, as in Egyptian ("logo-consonantal").
Some scripts, however, are truly ambiguous. The semi-syllabaries of ancient Spain were syllabic for plosives such as p, t, k, but alphabetic for other consonants. In some versions, vowels were written redundantly after syllabic letters, conforming to an alphabetic orthography. Old Persian cuneiform was similar. Of 23 consonants (including null), seven were fully syllabic, thirteen were purely alphabetic, and for the other three, there was one letter for /Cu/ and another for both /Ca/ and /Ci/. However, all vowels were written overtly regardless; as in the Brahmic abugidas, the /Ca/ letter was used for a bare consonant.
The zhuyin phonetic glossing script for Chinese divides syllables in two or three, but into onset, medial, and rime rather than consonant and vowel. Pahawh Hmong is similar, but can be considered to divide syllables into either onset-rime or consonant-vowel (all consonant clusters and diphthongs are written with single letters); as the latter, it is equivalent to an abugida but with the roles of consonant and vowel reversed. Other scripts are intermediate between the categories of alphabet, abjad, and abugida, so there may be disagreement on how they should be classified.
Graphic classification of writing systems
සංස්කරණයPerhaps the primary graphic distinction made in classifications is that of linearity. Linear writing systems are those in which the characters are composed of lines, such as the Latin alphabet and Chinese characters. Chinese characters are considered linear whether they're written with a ball-point pen or a calligraphic brush, or cast in bronze. Similarly, Egyptian hieroglyphs and Maya glyphs were often painted in linear outline form, but in formal situations they were carved in bas-relief. Non-linear systems, on the other hand, such as braille, are not composed of lines, no matter which instrument is used to write them. The earliest examples of writing are linear: the Sumerian script of c. 3300 BCE was linear, though its cuneiform descendants were not.
Cuneiform was probably the earliest non-linear writing. Its glyphs were formed by pressing the end of a reed stylus into moist clay, not by tracing lines in the clay with the stylus as had been done previously. The result was a radical transformation of the appearance of the script.
Braille is a non-linear adaptation of the Latin alphabet that completely abandoned the Latin forms. The letters are composed of raised bumps on the writing substrate, which can be leather (Louis Braille's original material), stiff paper, plastic, or metal.
There are also transient non-linear adaptations of the Latin alphabet, including Morse code, the manual alphabets of various sign languages, and semaphore, in which flags or bars are positioned at prescribed angles. However, if "writing" is defined as a potentially permanent means of recording information, then these systems do not qualify as writing at all, since the symbols disappear as soon as they are used.
If the Edo script is indeed a complete writing system, it may be the only natural example of a script in which the color of the graphemes is contrastive.
Directionality
සංස්කරණයScripts are also graphically characterized by the direction in which they are written. Egyptian hieroglyphs were written in either horizontal direction, with the animal and human glyphs turned to face the beginning of the line. The early alphabet could be written in multiple directions,[තහවුරු කර නොමැත] horizontally (left-to-right or right-to-left) or vertically (up or down). It was commonly written boustrophedonically: starting in one (horizontal) direction, then turning at the end of the line and reversing direction.
The Greek alphabet and its successors settled on a left-to-right pattern, from the top to the bottom of the page. In Timed Text (TT) Authoring Format, this pattern is abbreviated LRTB.[2] Other scripts, such as Arabic and Hebrew, came to be written right-to-left. Scripts that incorporate Chinese characters have traditionally been written vertically (top-to-bottom), from the right to the left of the page, but nowadays are frequently written left-to-right, top-to-bottom, due to Western influence, a growing need to accommodate terms in the Roman alphabet, and technical limitations in popular electronic document formats. The Uighur alphabet and its descendants are unique in being the only scripts written top-to-bottom, left-to-right; this direction originated from an ancestral Semitic direction by rotating the page 90° counter-clockwise to conform to the appearance of vertical Chinese writing. Several scripts used in the Philippines and ඉන්දුනීසියාව, such as Hanunó'o, are traditionally written with lines moving away from the writer, from bottom to top, but are read horizontally left to right.
Writing systems on computers
සංස්කරණයDifferent ISO/IEC standards are defined to deal with each individual writing systems to implement them in computers (or in electronic form). Today most of those standards are re-defined in a better collective standard, the ISO 10646, also known as Unicode. In Unicode, each character, in every language's writing system, is (simplifying slightly) given a unique identification number, known as its code point. The computer's software uses the code point to look up the appropriate character in the font file, so the characters can be displayed on the page or screen.
A keyboard is the device most commonly used for writing via computer. Each key is associated with a standard code which the keyboard sends to the computer when it is pressed. By using a combination of alphabetic keys with modifier keys such as Ctrl, Alt, Shift and AltGr, various character codes are generated and sent to the CPU. The operating system intercepts and converts those signals to the appropriate characters based on the keyboard layout and input method, and then delivers those converted codes and characters to the running application software, which in turn looks up the appropriate glyph in the currently used font file, and requests the operating system to draw these on the screen.
In computers and telecommunication systems, graphemes and other grapheme-like units that are required for text processing are represented by "characters" that typically manifest in encoded form. For technical aspects of computer support for various writing systems, see Universal Character Set, CJK (Chinese, Japanese, Korean) and Bi-directional text, as well as Category:Character encoding.
See also
සංස්කරණය- Artificial script
- Asemic writing
- Calligraphy
- Font
- Formal language
- Genealogy of scripts derived from Proto-Sinaitic
- History of writing
- History of writing numbers
- ISO 15924 — a list of "codes for the representation of names of scripts"
- List of inventors of writing systems
- List of writing systems
- Lower case
- Majuscule
- Nü Shu
- Official script
- Orthography
- Pasigraphy
- Penmanship
- Shorthand
- Spelling
- Transliteration
- Universal Character Set
- Written language
References
සංස්කරණය- Coulmas, Florian. 1996. The Blackwell encyclopedia of writing systems. Oxford: Blackwell.
- Daniels, Peter T., and William Bright, eds. 1996. The World's Writing Systems. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-507993-0.
- DeFrancis, John. 1990. The Chinese Language: Fact and Fantasy. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-1068-6
- Hannas, William. C. 1997. Asia's Orthographic Dilemma. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 0-8248-1892-X (paperback); ISBN 0-8248-1842-3 (hardcover)
- Rogers, Henry. 2005. Writing Systems: A Linguistic Approach. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-23463-2 (hardcover); ISBN 0-631-23464-0 (paperback)
- Sampson, Geoffrey. 1985. Writing Systems. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-1756-7 (paper), ISBN 0-8047-1254-9 (cloth).
- Smalley, W. A. (ed.) 1964. Orthography studies: articles on new writing systems. London: United Bible Society.
External links
සංස්කරණය- Arch Chinese (Traditional & Simplified) Chinese character writing animations and native speaker pronunciations
- decodeunicode Unicode Wiki with all 98,884 Unicode 5.0 characters as gifs in three sizes
- African writing systems
- Omniglot
- [1] සංරක්ෂණය කළ පිටපත 2011-02-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Ancient Scripts Introduction to different writing systems
- Michael Everson's Alphabets of Europe
- The Unicode Consortium