බැර ජලය
ඩියුටේරියම් ඔක්සයිඩ් හෝ 2H2O හෝ D2O ලෙසින් මුලින් හැඳින්වුනු, බැර ජලය යනු, සාමාන්ය ජලයේ බොහෝ හයිඩ්රජන් ප්රමාණයක අඩංගු වන පොදුවේ පවතින හයිඩ්රජන්-1 සමස්ථානිකය වෙනුවට, සාමාන්ය ප්රමාණයට වඩා වැඩි ප්රමාණයක්, ඩියුටේරියම් ("බැර හයිඩ්රජන්" ලෙසින්ද හැඳින්වෙන) නම් හයිඩ්රජන් සමස්ථානිකය අඩංගු වන, ජලය ආකාරයකි.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2H2)Water[3]
| |||
| වෙනත් නාම | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS number | {{{value}}} | ||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:{{{value}}} | ||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.226 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 97 | |||
| KEGG | {{{value}}} | ||
| MeSH | {{{value}}} | ||
| PubChem | {{{value}}} | ||
| RTECS number | {{{value}}} | ||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
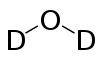
| Molecular formula | D2O | ||
| අණුක ස්කන්ධය | 20.0276 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 1.107 g mL−1 | ||
| Melting point |
4 °C, 276.97 K, 39 °F | ||
| Boiling point |
101.4 °C, 375 K, 215 °F | ||
| Solubility in water | Miscible | ||
| log P | −1.38 | ||
| Solubility product, Ksp | 1.328 | ||
| Viscosity | 1.25 mPa s (at 20 °C) | ||
| 1.87 D | |||
| Hazards | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||

ආශ්රිත
සංස්කරණයමූලාශ්ර
සංස්කරණය- ^ Parpart, Arthur K. (December 1935). "The permeability of the mammalian erythrocyte to deuterium oxide (heavy water)". Journal of Cellular and Comparative Physiology. 7 (2): 153–162. doi:10.1002/jcp.1030070202.
- ^ Svishchev, I. M.; Kusalik, P. G. (January 1994). "Dynamics in liquid water, water-d2, and water-t2: a comparative simulation study". The Journal of Physical Chemistry. 98 (3): 728–733. doi:10.1021/j100054a002.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2005). Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2005). Cambridge (UK): RSC–IUPAC. ISBN 0-85404-438-8. p. 306. Electronic version.