බ්රිතාන්ය ඉන්දියාව
ක්රිස්තු වර්ශ 1612 සහ 1947 අතර කාලය තුල පෙරදිග ඉන්දීය සමාගමට හෝ බ්රිතාන්ය රජහට අයත්ව තිබූ ඉන්දියාව සහ ආශ්රිත පරිපාලන කලාප බ්රිතාන්ය ඉන්දියාව නමින් පොදුවේ හැඳින්විනි.
- ^ Interpretation Act 1889 (52 & 53 Vict. c. 63), s. 18.
- ^ "Calcutta (Kalikata)", The Imperial Gazetteer of India, IX Bomjur to Central India, Published under the Authority of His Majesty's Secretary of State for India in Council, Oxford at the Clarendon Press, 1908, p. 260, http://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?volume=9&objectid=DS405.1.I34_V09_266.gif, "—Capital of the Indian Empire, situated in 22° 34' N and 88° 22' E, on the east or left bank of the Hooghly river, within the Twenty-four Parganas District, Bengal"
- ^ "Simla Town", The Imperial Gazetteer of India, XXII Samadhiāla to Singhāna, Published under the Authority of His Majesty's Secretary of State for India in Council, Oxford at the Clarendon Press, 1908, p. 260, http://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/pager.html?objectid=DS405.1.I34_V09_266.gif, "—Head-quarters of Simla District, Punjab, and the summer capital of the Government of India, situated on a transverse spur of the Central Himālayan system system, in 31° 6' N and 77° 10' E, at a mean elevation above sea-level of 7,084 feet."
- ^ Vejdani, Farzin (2015), Making History in Iran: Education, Nationalism, and Print Culture, Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, pp. 24–25, , "Although the official languages of administration in India shifted from Persian to English and Urdu in 1837, Persian continued to be taught and read there through the early twentieth century."
- ^ Everaert, Christine (2010), Tracing the Boundaries between Hindi and Urdu, Leiden and Boston: BRILL, pp. 253–254, , "It was only in 1837 that Persian lost its position as official language of India to Urdu and to English in the higher levels of administration."
ඉන්දියාව | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1858–1947 | |||||||||||||
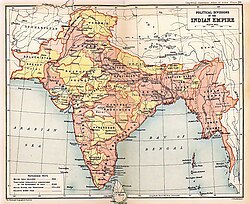 1909 Map of India, showing British India in two shades of pink and Princely states in yellow | |||||||||||||
| තත්ත්වය | Imperial political structure (comprising British India[a] සහ කුමාරධානි.[b]).[1] | ||||||||||||
| අගනුවර | කල්කටා[2][c] (1858–1911) New Delhi (1911/1931[d]–1947) | ||||||||||||
| නිල භාෂා(ව) | English and Urdu[4][5] | ||||||||||||
| රජය | British Colonial Government | ||||||||||||
| King-Emperor/Queen-Empress | |||||||||||||
• 1858–1901 | වික්ටෝරියා රැජිණ | ||||||||||||
• 1901–1910 | Edward VII | ||||||||||||
• 1910–1936 | George V | ||||||||||||
• 1936 | Edward VIII | ||||||||||||
• 1936–1947 | හයවන ජෝර්ජ් රජ | ||||||||||||
| Viceroy | |||||||||||||
• 1858–1862 (first) | Charles Canning | ||||||||||||
• 1947 (last) | Louis Mountbatten | ||||||||||||
| Secretary of State | |||||||||||||
• 1858–1859 (first) | Edward Stanley | ||||||||||||
• 1947 (last) | William Hare | ||||||||||||
| ව්යවස්ථාදායකය | Imperial Legislative Council | ||||||||||||
| ඉතිහාසය | |||||||||||||
| 10 May 1857 | |||||||||||||
| 2 August 1858 | |||||||||||||
| 18 July 1947 | |||||||||||||
| 14 and 15 August 1947 | |||||||||||||
| ව්යවහාර මුදල | Indian rupee | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||