ගොනුව:Lens and wavefronts.gif
Lens_and_wavefronts.gif (183 × 356 පික්සල, ගොනු විශාලත්වය: 35 කි.බ., MIME ශෛලිය: image/gif, වලිත, 9 රාමු, 0.7තත්)
ගොනු ඉතිහාසය
එම අවස්ථාවෙහිදී ගොනුව පැවැති ආකාරය නැරඹීමට දිනය/වේලාව මත ක්ලික් කරන්න.
| දිනය/වේලාව | කුඩා-රූපය | මාන | පරිශීලක | පරිකථනය | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| වත්මන් | 06:35, 25 නොවැම්බර් 2007 |  | 183 × 356 (35 කි.බ.) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak |
| 04:10, 24 නොවැම්බර් 2007 |  | 171 × 356 (33 කි.බ.) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak | |
| 04:09, 24 නොවැම්බර් 2007 |  | 171 × 356 (33 කි.බ.) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak | |
| 00:56, 24 නොවැම්බර් 2007 |  | 171 × 359 (33 කි.බ.) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak, same license | |
| 00:53, 24 නොවැම්බර් 2007 | 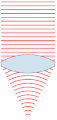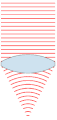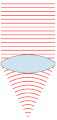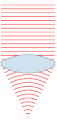 | 171 × 359 (32 කි.බ.) | Oleg Alexandrov | tweak | |
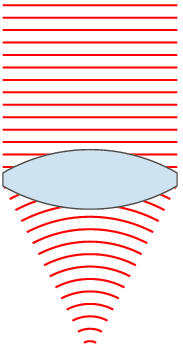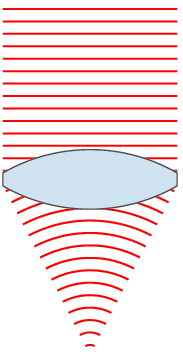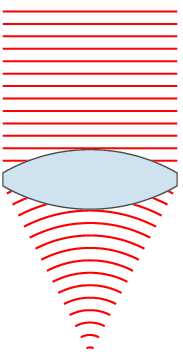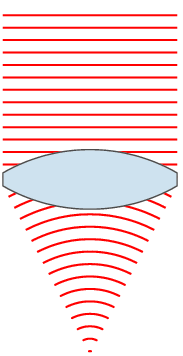
| 00:49, 24 නොවැම්බර් 2007 |  | 151 × 359 (31 කි.බ.) | Oleg Alexandrov | {{Information |Description=Illustration of wavefronts after passing through a [:en:lens (optics)|lens]] |Source=self-made with MATLAB |Date=~~~~~ |Author= Oleg Alexandrov |Permission=see below |other_versions= }} |
ගොනු භාවිතය
පහත දැක්වෙන පිටුව විසින් මෙම ගොනුව භාවිතා කෙරෙයි:
ගෝලීය ගොනු භාවිතය
පහත දැක්වෙන අනෙකුත් විකියන් මගින් මෙම ගොනුව භාවිතා කරයි:
- ar.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- ast.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- be.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- bn.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- bs.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- ckb.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- cs.wikiversity.org හි භාවිතය
- cv.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- en.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- en.wikiversity.org හි භාවිතය
- es.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- es.wikiversity.org හි භාවිතය
- eu.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- fa.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- fi.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- fr.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- fr.wikibooks.org හි භාවිතය
- fy.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- ga.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- he.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- hi.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- hr.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- hy.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- id.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- lt.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- lv.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- ml.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- mn.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- nl.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- pa.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- ru.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- sh.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- sl.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- sr.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- sv.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
- ta.wikipedia.org හි භාවිතය
මෙම ගොනුවේ තවත් ගෝලීය භාවිත බලන්න.